In Transcription Within the Nucleus Rna Is Made Through
RNA polymerase I is located in the nucleolus a specialized nuclear substructure in which ribosomal RNA rRNA is transcribed processed and assembled into ribosomes Table 1. In the process of translation A a strand of mRNA is formed with nucleotide sequences complementary to those of DNA.
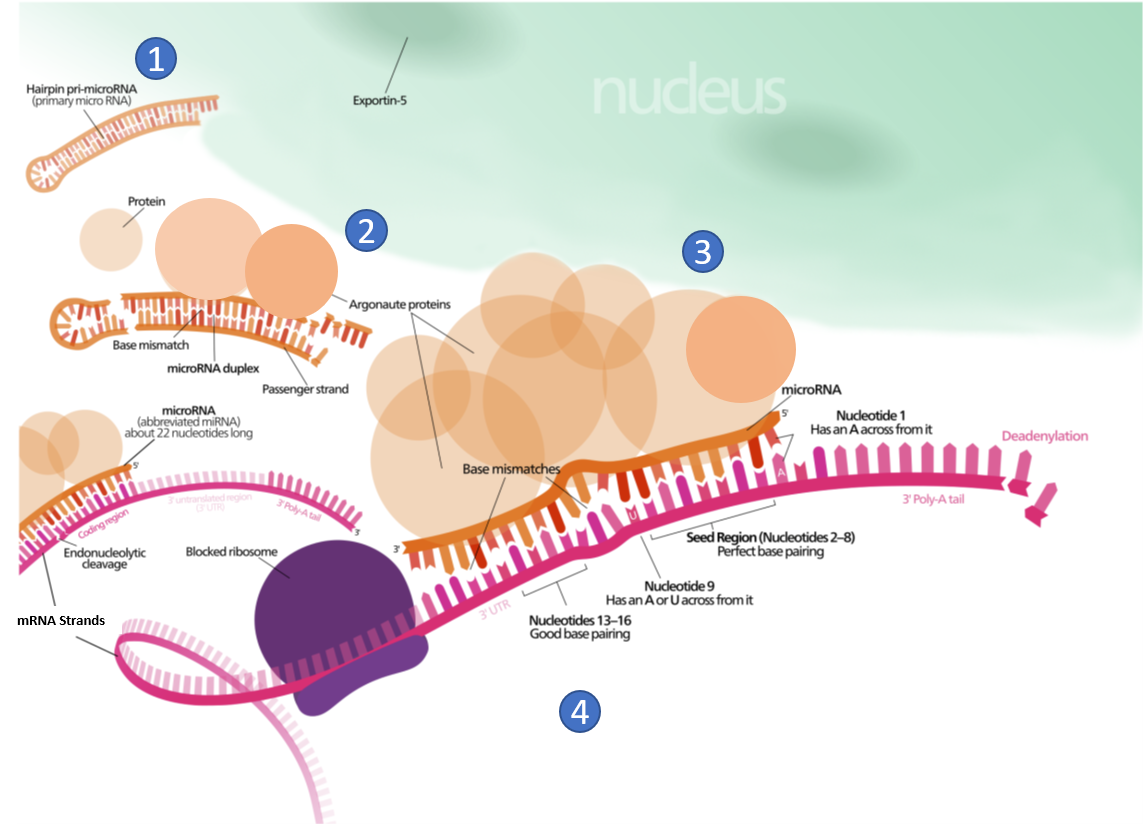
Chapter 10 Transcription And Rna Processing Chemistry
Transcription takes place in the nucleus.

. The RNA polymerase is the main enzyme involved in transcription. In eukaryotes transcription and modification of mRNA happens exclusively in the nucleus. Termination- polymerase stops transcribing the gene 4.
Process through which RNA is formed along a DNA template. When DNA is tightly wound twice around a nucleosome RNA Polymerase II cannot access it for transcription. This mRNA then exits the nucleus where it acts as the basis for the translation of DNA.
After which pre-mRNA undergoes RNA. After mRNA processing the mature mRNA travels out of the nucleus through a nuclear pore. As seen with Nup98 mobility of Nup153 is arrested in the presence of transcription inhibitors although transcription-dependent dynamics are mediated by distinct domains within each protein.
-DNA molecule remains within the safety of the nucleus while RNA molecules go to the protein- building sites in the cytoplasm- the ribosomes. Initiation- polymerase binds to the gene 2. Transcription is the process where DNA is used to create mRNA.
DNA terminator sequence is transcribed by RNA polymerase RNA to fold and causes RNA polymerase to release grip on DNA 2 enzyme dependent termination. In transcription an mRNA messenger RNA intermediate is transcribed from one of the strands of the DNA molecule. Elongation- polymerase transcribes the gene 3.
The FACT protein dimer allows RNA Polymerase II to transcribe through packaged DNA. The other strand is called the noncoding strand or nontemplate strand. How DNA is different from RNA.
In the cytosol the liquid body of the cell outside the nucleus the mature mRNA attaches to a ribosome and goes through translation. During transcription RNA polymerase II is aided by specific factors as it encounters numerous blocks to elongation inherent in a template sequence. RNA polymerase constructs DNA using the template strand or antisense strand.
RNA and DNA use complementary coding where base pairs match up similar. The enzyme RNA polymerase catalyzes the formation of RNA from ribonucleoside triphosphates. Pre-mRNA is actually created first through 3 processes initiation elongation and termination.
Processing- pre mRNA mature mRNA is formed 5. RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA using the antisense strand of the DNA as template by adding complementary RNA nucleotides to the 3 end of the growing strand. RNA polymerase binds to DNA at a sequence called a promoter during the initiation of transcription.
It uses DNA as a template to make an RNA mRNA molecule. RNA Nitrogenous bases. The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5 to 3 direction on the template strand.
Transcription could be critical because the dynamic association of these nucleoporins with the pore is coupled to movement of RNA cargo through the pore. RNA polymerase binds to DNA at a sequence called a promoter during the initiation of transcription. C a polypeptide is formed in response to the rRNA nucleotide sequence.
Termination enzyme Rho pushes between RNA polymerase and DNA forces them apart. In this image Nitrogenous base options for DNA and RNA. The mRNA synthesized is then transported out of the cells nucleus to assist in the production of proteins via the mechanism of translation.
DNA transcription is the process by which the genetic information contained within DNA is re-written into messenger RNA mRNA by RNA polymerase. Wiki Practice the transcription of DNA to RNA. B nucleotide sequences of tRNA are established.
DNA in eukaryotes is packaged in nucleosomes which consist of an octomer of 4 different histone proteins. It uses single-strand DNA to synthesize a complementary RNA strand. The process of DNA transcription also referred to as RNA synthesis is the process where genetic information in DNA is transformed into messenger mRNA mRNA through an enzyme known as RNA polymerase.
In our cell the transcription is done by an enzyme called RNA polymerase in the nucleus which can synthesize mRNA from a DNA template. The rRNA molecules are considered structural RNAs because they have a cellular role but are not translated into protein. Figure 1 shows how this occurs.
During transcription the information encoded in DNA is used to make RNA. D rRNA is synthesized with sequences complementary to those of tRNA. RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA using the antisense strand of the DNA as template by adding complementary RNA nucleotides to the 3 end of the growing strand.
By controlling the production of mRNA within the nucleus the cell regulates the rate of gene expressionIn this article we will. Translation Protein polypeptide synthesis directed by a specific mRNA. Steps of RNA synthesis 1.
Transcript The RNA molecule produced by transcription of a gene. Once it reaches the terminator sequence the process terminates and the. During normal transcription in vivo each nucleotide addition to an RNA chain requires 50 ms on average.
During transcription a strand of mRNA is made that is complementary to a strand of DNA. The RNA is called messenger RNA because it carries the message or genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes where the information is used to make proteins. During transcription the information encoded in DNA is used to make RNA.
-Made of Nucleotides-Carry info for protein synthesis.
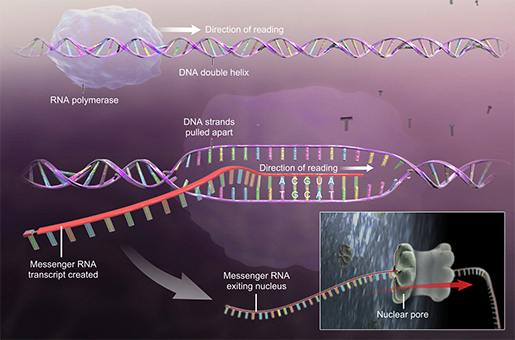
Dna And Rna Basics Replication Transcription And Translation

The Transcription Of Life From Dna To Rna Frontiers For Young Minds
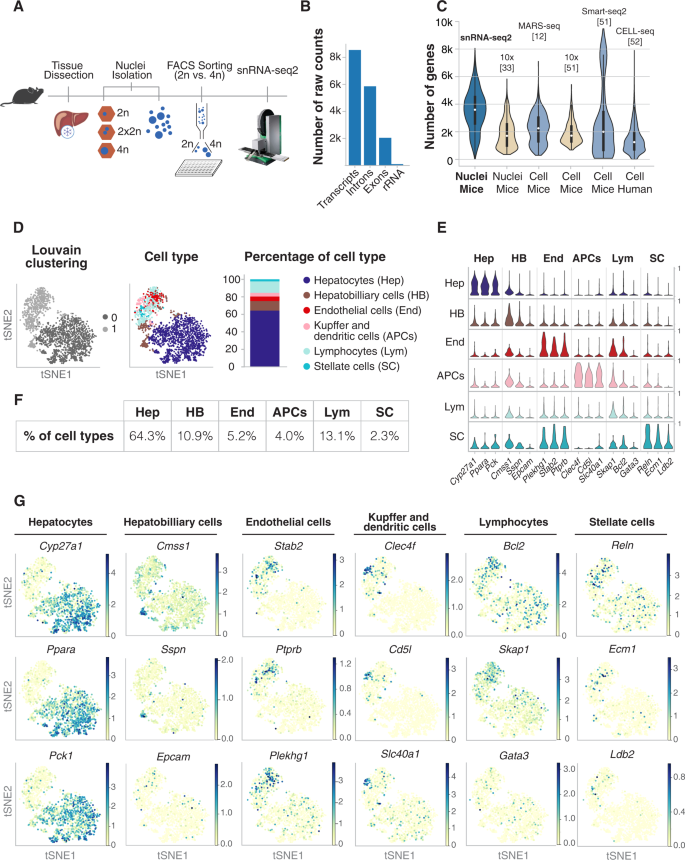
Single Nucleus Rna Seq2 Reveals Functional Crosstalk Between Liver Zonation And Ploidy Nature Communications

Gene Expression Central Dogma Of Molecular Biology Eps8 Ad Central Expression Gene Dogma Biolo Biologie Biologie Cellulaire Dictionnaire Medical

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks

Pin On Cells Organelles Dna Rna
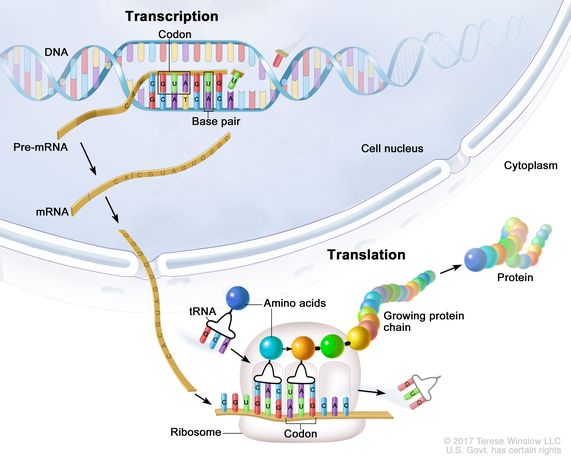
Definition Of Transcription Nci Dictionary Of Genetics Terms National Cancer Institute

Discovery Of Chemical Structure Of Dna February 28 1953 Biology Activity Teaching Biology Biology Classroom

Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica

Life Dna Rna And Protein Britannica

Rna Polymerase Function And Definition Technology Networks

Presentation Notes Chapter 13 Rna Protein Synthesis 2 Steps Transcription Dna Is Made Into Mrna In The Nuc Teacher Evaluation Texas Teacher Chapter 13

Dissecting Cell Type Composition And Activity Dependent Transcriptional State In Mammalian Brains By Massively Parallel Single Nucleus Rna Seq Molecular Cell





Comments
Post a Comment